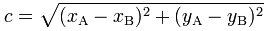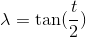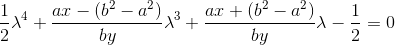расстояние от заданной точки до заданного эллипса
У меня есть эллипс, определенный центральной точкой, radiusX и radiusY, и у меня есть точка. Я хочу найти точку на эллипсе, который ближе всего к данной точке. На рисунке ниже это будет S1.
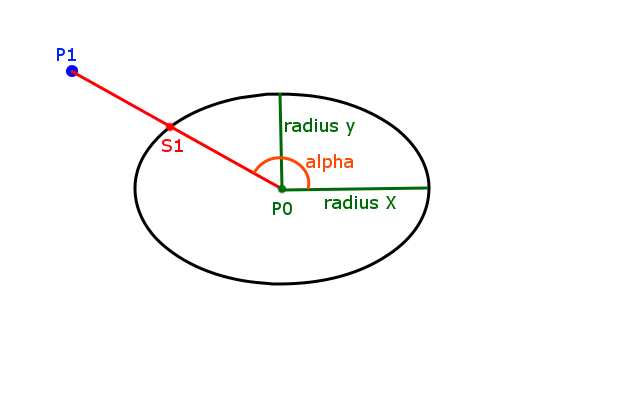
теперь у меня уже есть код, но где-то в нем есть логическая ошибка, и я, кажется, не могу ее найти. Я разбил проблему на следующий пример кода:
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
void dostuff();
int main()
{
dostuff();
return 0;
}
typedef std::vector<cv::Point> vectorOfCvPoints;
void dostuff()
{
const double ellipseCenterX = 250;
const double ellipseCenterY = 250;
const double ellipseRadiusX = 150;
const double ellipseRadiusY = 100;
vectorOfCvPoints datapoints;
for (int i = 0; i < 360; i+=5)
{
double angle = i / 180.0 * CV_PI;
double x = ellipseRadiusX * cos(angle);
double y = ellipseRadiusY * sin(angle);
x *= 1.4;
y *= 1.4;
x += ellipseCenterX;
y += ellipseCenterY;
datapoints.push_back(cv::Point(x,y));
}
cv::Mat drawing = cv::Mat::zeros( 500, 500, CV_8UC1 );
for (int i = 0; i < datapoints.size(); i++)
{
const cv::Point & curPoint = datapoints[i];
const double curPointX = curPoint.x;
const double curPointY = curPoint.y * -1; //transform from image coordinates to geometric coordinates
double angleToEllipseCenter = atan2(curPointY - ellipseCenterY * -1, curPointX - ellipseCenterX); //ellipseCenterY * -1 for transformation to geometric coords (from image coords)
double nearestEllipseX = ellipseCenterX + ellipseRadiusX * cos(angleToEllipseCenter);
double nearestEllipseY = ellipseCenterY * -1 + ellipseRadiusY * sin(angleToEllipseCenter); //ellipseCenterY * -1 for transformation to geometric coords (from image coords)
cv::Point center(ellipseCenterX, ellipseCenterY);
cv::Size axes(ellipseRadiusX, ellipseRadiusY);
cv::ellipse(drawing, center, axes, 0, 0, 360, cv::Scalar(255));
cv::line(drawing, curPoint, cv::Point(nearestEllipseX,nearestEllipseY*-1), cv::Scalar(180));
}
cv::namedWindow( "ellipse", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
cv::imshow( "ellipse", drawing );
cv::waitKey(0);
}
производит следующие изображение:
вы можете видеть, что он действительно находит "близкие" точки на эллипсе, но это не "ближайшие" точки. Что я намеренно хочу, так это: (извините мой бедный рисунок)
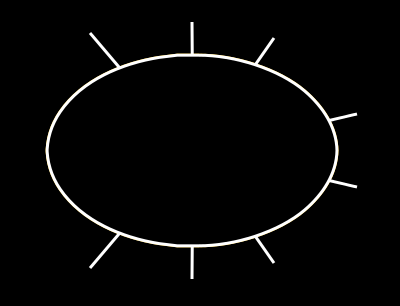
вы бы расширили линии на последнем изображении, они пересекли бы центр эллипса, но это не относится к линиям на предыдущем изображении.
Надеюсь, вы поняли. Может кто-нибудь сказать мне, что я делаю неправильно?
6 ответов
рассмотрим ограничивающую окружность вокруг данной точки (c, d), которая проходит через ближайшую точку на эллипсе. Из диаграммы ясно, что ближайшая точка такова, что линия, проведенная от нее до данной точки, должна быть перпендикулярна общей касательной эллипса и окружности. Любые другие точки будут находиться вне круга и поэтому должны быть дальше от данной точки.

Так что вы ищете не в пересечение между линией и эллипсом, но точкой (x, y) на диаграмме.
градиент касательной:
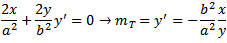
градиент строку:
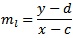
условие для перпедикулярных линий-произведение градиентов = -1:
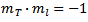
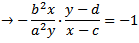
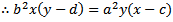
при перестановке и замене в уравнение вашего эллипс...
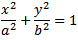
...это даст два неприятных квартичных (полиномиальных) уравнения 4-й степени в терминах x или y. AFAIK нет общие аналитические (точные алгебраические) методы их решения. Вы можете попробовать итерационный метод-найти итерационный алгоритм поиска корней Ньютона-Рафсона.
взгляните на эту очень хорошую бумагу на предмет:: http://www.spaceroots.org/documents/distance/distance-to-ellipse.pdf
извините за неполный ответ - я полностью обвиняю законы математики и природы...
EDIT: ой, кажется, у меня есть a и b неправильно в диаграмме xD
вот код, переведенный на C#, реализованный из этой статьи, чтобы решить для эллипса: http://www.geometrictools.com/Documentation/DistancePointEllipseEllipsoid.pdf
обратите внимание, что этот код непроверен - если вы найдете какие-либо ошибки, дайте мне знать.
//Pseudocode for robustly computing the closest ellipse point and distance to a query point. It
//is required that e0 >= e1 > 0, y0 >= 0, and y1 >= 0.
//e0,e1 = ellipse dimension 0 and 1, where 0 is greater and both are positive.
//y0,y1 = initial point on ellipse axis (center of ellipse is 0,0)
//x0,x1 = intersection point
double GetRoot ( double r0 , double z0 , double z1 , double g )
{
double n0 = r0*z0;
double s0 = z1 - 1;
double s1 = ( g < 0 ? 0 : Math.Sqrt(n0*n0+z1*z1) - 1 ) ;
double s = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < maxIter; ++i ){
s = ( s0 + s1 ) / 2 ;
if ( s == s0 || s == s1 ) {break; }
double ratio0 = n0 /( s + r0 );
double ratio1 = z1 /( s + 1 );
g = ratio0*ratio0 + ratio1*ratio1 - 1 ;
if (g > 0) {s0 = s;} else if (g < 0) {s1 = s ;} else {break ;}
}
return s;
}
double DistancePointEllipse( double e0 , double e1 , double y0 , double y1 , out double x0 , out double x1)
{
double distance;
if ( y1 > 0){
if ( y0 > 0){
double z0 = y0 / e0;
double z1 = y1 / e1;
double g = z0*z0+z1*z1 - 1;
if ( g != 0){
double r0 = (e0/e1)*(e0/e1);
double sbar = GetRoot(r0 , z0 , z1 , g);
x0 = r0 * y0 /( sbar + r0 );
x1 = y1 /( sbar + 1 );
distance = Math.Sqrt( (x0-y0)*(x0-y0) + (x1-y1)*(x1-y1) );
}else{
x0 = y0;
x1 = y1;
distance = 0;
}
}
else // y0 == 0
x0 = 0 ; x1 = e1 ; distance = Math.Abs( y1 - e1 );
}else{ // y1 == 0
double numer0 = e0*y0 , denom0 = e0*e0 - e1*e1;
if ( numer0 < denom0 ){
double xde0 = numer0/denom0;
x0 = e0*xde0 ; x1 = e1*Math.Sqrt(1 - xde0*xde0 );
distance = Math.Sqrt( (x0-y0)*(x0-y0) + x1*x1 );
}else{
x0 = e0;
x1 = 0;
distance = Math.Abs( y0 - e0 );
}
}
return distance;
}
существует относительно простой численный метод с лучшей сходимостью, чем метод Ньютона. У меня есть сообщение в блоге о том, почему он работаетhttp://wet-robots.ghost.io/simple-method-for-distance-to-ellipse/
эта реализация работает без каких-либо тригонометрические функции:
def solve(semi_major, semi_minor, p):
px = abs(p[0])
py = abs(p[1])
tx = 0.707
ty = 0.707
a = semi_major
b = semi_minor
for x in range(0, 3):
x = a * tx
y = b * ty
ex = (a*a - b*b) * tx**3 / a
ey = (b*b - a*a) * ty**3 / b
rx = x - ex
ry = y - ey
qx = px - ex
qy = py - ey
r = math.hypot(ry, rx)
q = math.hypot(qy, qx)
tx = min(1, max(0, (qx * r / q + ex) / a))
ty = min(1, max(0, (qy * r / q + ey) / b))
t = math.hypot(ty, tx)
tx /= t
ty /= t
return (math.copysign(a * tx, p[0]), math.copysign(b * ty, p[1]))
кредит Эдриан Стивенс на Trig-Бесплатная Оптимизация.
следующий код python реализует уравнения, описанные в "расстояние от точки до эллипса " и использует метод Ньютона, чтобы найти корни и от этого ближайшую точку на эллипсе к точке.
к сожалению, как видно из примера, он кажется точным только вне эллипса. Внутри эллипса происходят странные вещи.
from math import sin, cos, atan2, pi, fabs
def ellipe_tan_dot(rx, ry, px, py, theta):
'''Dot product of the equation of the line formed by the point
with another point on the ellipse's boundary and the tangent of the ellipse
at that point on the boundary.
'''
return ((rx ** 2 - ry ** 2) * cos(theta) * sin(theta) -
px * rx * sin(theta) + py * ry * cos(theta))
def ellipe_tan_dot_derivative(rx, ry, px, py, theta):
'''The derivative of ellipe_tan_dot.
'''
return ((rx ** 2 - ry ** 2) * (cos(theta) ** 2 - sin(theta) ** 2) -
px * rx * cos(theta) - py * ry * sin(theta))
def estimate_distance(x, y, rx, ry, x0=0, y0=0, angle=0, error=1e-5):
'''Given a point (x, y), and an ellipse with major - minor axis (rx, ry),
its center at (x0, y0), and with a counter clockwise rotation of
`angle` degrees, will return the distance between the ellipse and the
closest point on the ellipses boundary.
'''
x -= x0
y -= y0
if angle:
# rotate the points onto an ellipse whose rx, and ry lay on the x, y
# axis
angle = -pi / 180. * angle
x, y = x * cos(angle) - y * sin(angle), x * sin(angle) + y * cos(angle)
theta = atan2(rx * y, ry * x)
while fabs(ellipe_tan_dot(rx, ry, x, y, theta)) > error:
theta -= ellipe_tan_dot(
rx, ry, x, y, theta) / \
ellipe_tan_dot_derivative(rx, ry, x, y, theta)
px, py = rx * cos(theta), ry * sin(theta)
return ((x - px) ** 2 + (y - py) ** 2) ** .5
вот пример:
rx, ry = 12, 35 # major, minor ellipse axis
x0 = y0 = 50 # center point of the ellipse
angle = 45 # ellipse's rotation counter clockwise
sx, sy = s = 100, 100 # size of the canvas background
dist = np.zeros(s)
for x in range(sx):
for y in range(sy):
dist[x, y] = estimate_distance(x, y, rx, ry, x0, y0, angle)
plt.imshow(dist.T, extent=(0, sx, 0, sy), origin="lower")
plt.colorbar()
ax = plt.gca()
ellipse = Ellipse(xy=(x0, y0), width=2 * rx, height=2 * ry, angle=angle,
edgecolor='r', fc='None', linestyle='dashed')
ax.add_patch(ellipse)
plt.show()
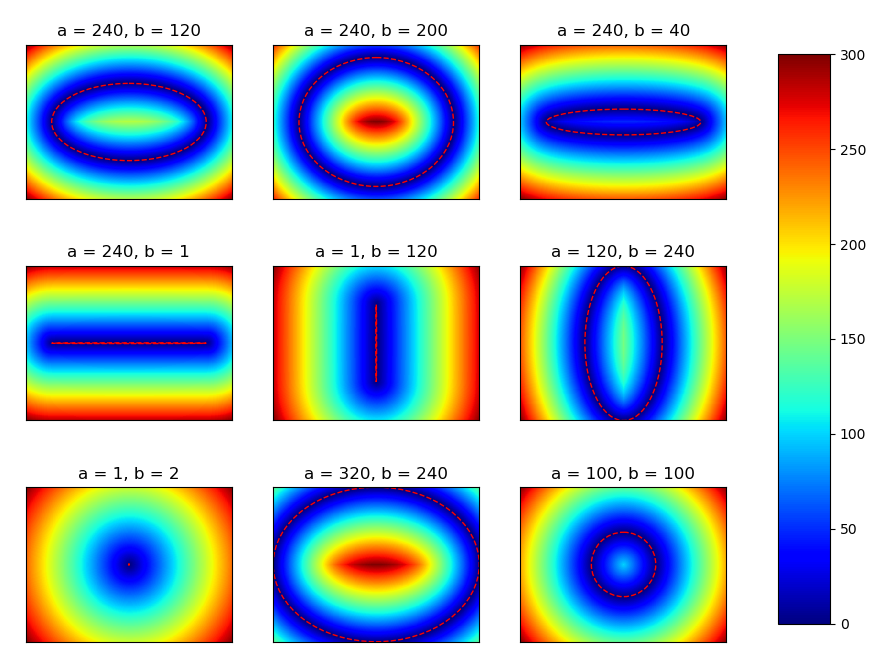
который генерирует 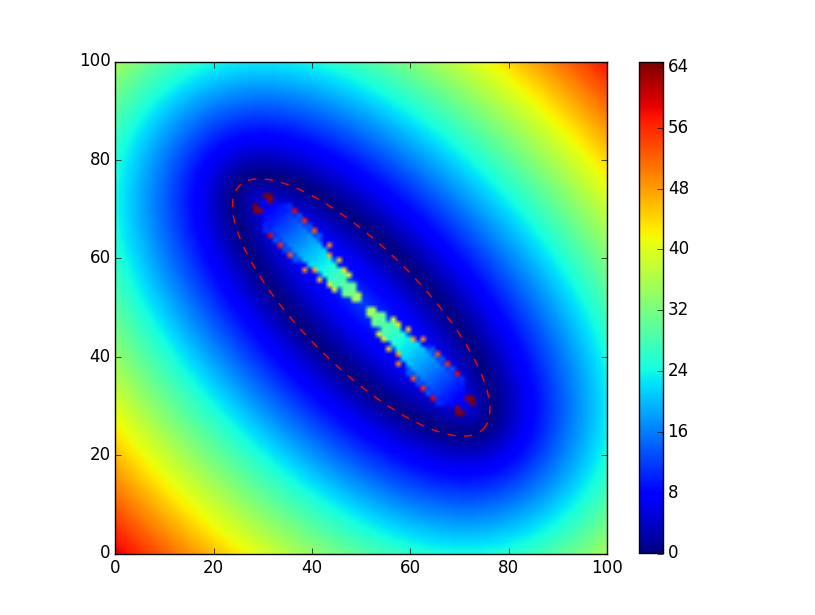 эллипса, а расстояние от границы эллипса как "тепловая карта". Как видно, на границе расстояние равно нулю (темно-синее).
эллипса, а расстояние от границы эллипса как "тепловая карта". Как видно, на границе расстояние равно нулю (темно-синее).
дан эллипс E в параметрической форме и точка P
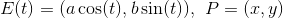
квадрат расстояния между P и E (t) is
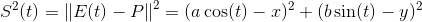
минимум должен удовлетворять
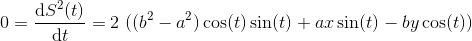
используя тригонометрические тождества
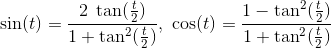
и заменить
дает следующее уравнение четвертой степени:
вот пример функции C, что решает квартик непосредственно и вычисляет sin (t) и cos (t) для ближайшей точки на эллипсе:
void nearest(double a, double b, double x, double y, double *ecos_ret, double *esin_ret) {
double ax = fabs(a*x);
double by = fabs(b*y);
double r = b*b - a*a;
double c, d;
int switched = 0;
if (ax <= by) {
if (by == 0) {
if (r >= 0) { *ecos_ret = 1; *esin_ret = 0; }
else { *ecos_ret = 0; *esin_ret = 1; }
return;
}
c = (ax - r) / by;
d = (ax + r) / by;
} else {
c = (by + r) / ax;
d = (by - r) / ax;
switched = 1;
}
double cc = c*c;
double D0 = 12*(c*d + 1); // *-4
double D1 = 54*(d*d - cc); // *4
double D = D1*D1 + D0*D0*D0; // *16
double St;
if (D < 0) {
double t = sqrt(-D0); // *2
double phi = acos(D1 / (t*t*t));
St = 2*t*cos((1.0/3)*phi); // *2
} else {
double Q = cbrt(D1 + sqrt(D)); // *2
St = Q - D0 / Q; // *2
}
double p = 3*cc; // *-2
double SS = (1.0/3)*(p + St); // *4
double S = sqrt(SS); // *2
double q = 2*cc*c + 4*d; // *2
double l = sqrt(p - SS + q / S) - S - c; // *2
double ll = l*l; // *4
double ll4 = ll + 4; // *4
double esin = (4*l) / ll4;
double ecos = (4 - ll) / ll4;
if (switched) {
double t = esin;
esin = ecos;
ecos = t;
}
*ecos_ret = copysign(ecos, a*x);
*esin_ret = copysign(esin, b*y);
}
вам просто нужно рассчитать пересечение линии [P1,P0] к вашему elipse который S1.
если equeation строка:
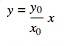
и elipse equesion:
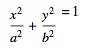
чем значения S1 будет:
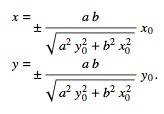
теперь вам просто нужно рассчитать расстояние между S1 to P1 формула (для A,B баллов) :